In the digital era, data is the new gold, and the cloud is the new frontier. As we embark on this journey through the cloud landscape, it is critical to understand the foundation upon which our data-driven aspirations are built. Just like a house needs a solid foundation before you can think about interior design, understanding the cloud’s data management structure is critical before you can tap into its full potential. In this article, we will break down the data management layers.
Exploring Data Management Layers
Imagine you are building a skyscraper. You wouldn’t start with a penthouse, would you? Similarly, when we talk about cloud data management, we have to start from the bottom and work our way up. Let’s explore the layers that form the backbone of any cloud-based data strategy.
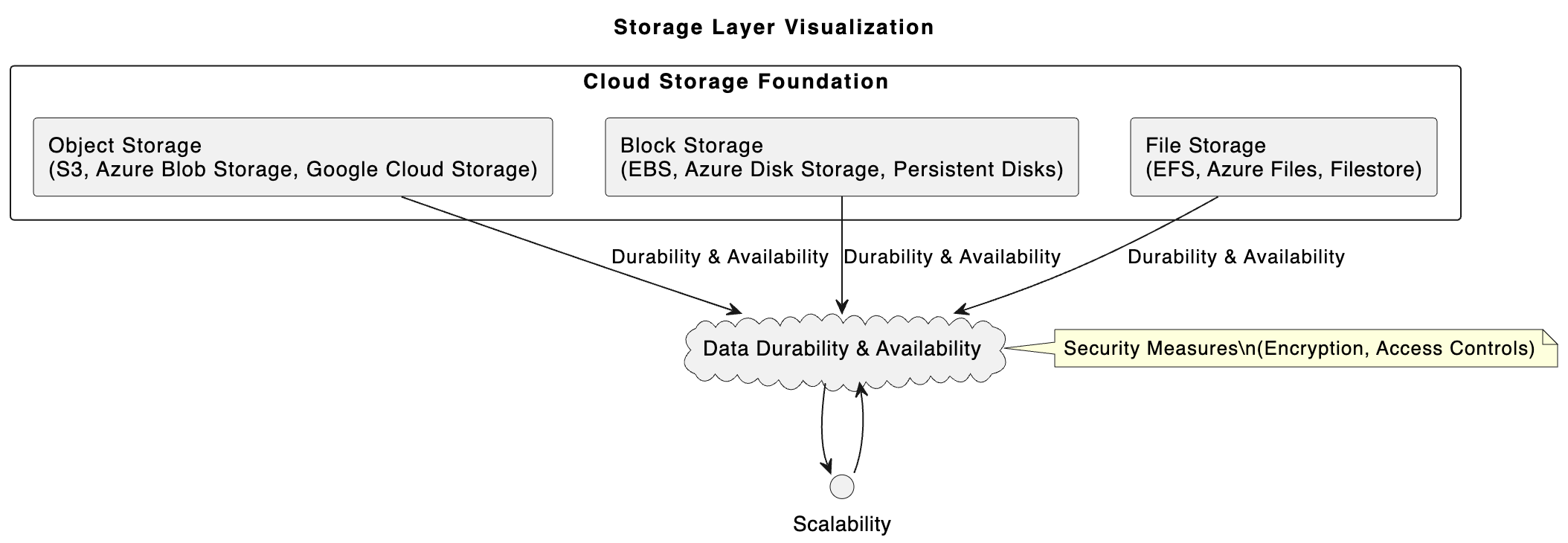
Storage layer
At the base of our data skyscraper is the storage layer. This is the digital equivalent of a building foundation. It’s where all your data sits, waiting to be called into action. However, not all storage is created equal. Just as you would choose a solid foundation for a house that will withstand the elements, you need secure, robust and scalable storage for your data.
Cloud storage solutions come in different flavors, such as object storage for unstructured data (think Amazon S3), block storage for structured data that requires frequent access (like Amazon EBS), and file storage for data that needs to be accessed via a file system (such as Amazon EFS).
Processing layer
Data, while at rest, is like an uncut diamond; hardworking but not yet flashy. The processing layer is where the magic happens. It is the engine that grinds the diamond, turning raw data into actionable insights. This layer includes all the calculations, transactions and transformations your data goes through.
Whether it’s a simple query or a complex machine learning algorithm, the processing layer is where your data is put to work. Cloud computing services such as Talend Cloud, Informatica Cloud for ETL processing, AWS Lambda for serverless computing or Airflow jobs for massive data analysis are prime examples of the power found within this layer.
Application layer
Climbing up, we reach the application layer. This is where tools and services come into play, allowing you to interact with your data. It is a floor with all content, databases, analytics software and content management systems.
In the cloud, services such as Amazon RDS for relational databases or Google Analytics for web analytics are part of this layer. They provide the interfaces and tools companies need to effectively manage, query, and manipulate data.
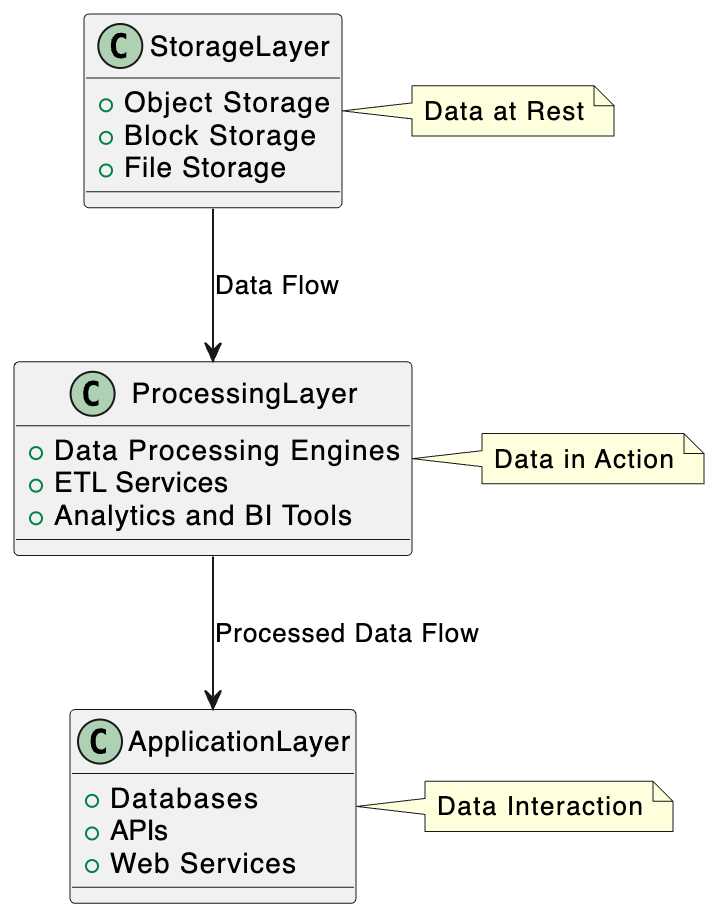
Presentation layer
At the top of our data skyscraper is the presentation layer. This is a grand lobby, a place where data is displayed in all its glory. It’s all about how the data is presented to the user, through dashboards, reports, visualizations or other interfaces.
The presentation layer is where data becomes available and understandable to decision makers. Tools like Tableau for data visualization or Power BI for business intelligence reports are part of this layer, turning complex data sets into clear, actionable insights.
Example: Retail dashboard for strategic insights
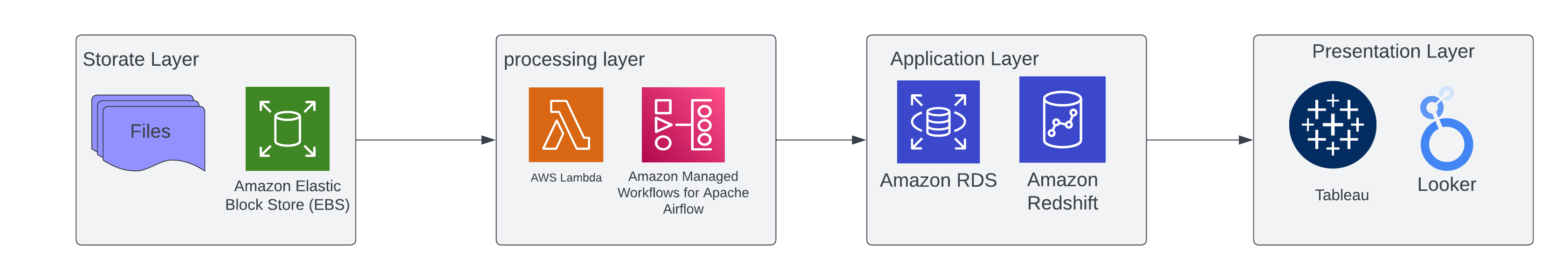
‘Trendsetter Boutique’ has created a dynamic dashboard within the presentation layer that embodies the synergy between storage, processing and application in cloud-based data management.
Initially, customer data and sales information resides in the storage layer, where raw numbers and facts reside in a safe place. In our example, they are available in Files and AWS Elastic Block Storage.
When processed at the processing layer through tools such as ETL pipelines and analytics engines, this data is transformed into valuable data using AWS lambda or Airflow jobs.
From there, insights ascend to the application layer where they are managed by cloud databases such as AWS Redshift Snowflake or AWS RDS, providing structure and accessibility to the collected information.
The final visual representation appears in the presentation layer. This is where Trendsetter’s dashboard (Tableau or Looker) comes into full swing, displaying real-time sales trends and customer data through intuitive charts and graphs. This allows managers to not only track current performance, but also anticipate market changes, making the dashboard an indispensable tool for the boutique’s data-driven decision-making process.
Below is a visual representation of the layers for ‘Trendsetter Boutique’.
Data protection in the cloud
With the cloud data management structure in place, it’s time to talk about security. After all, what good is a skyscraper if it’s not safe? Data security in the cloud is a multifaceted challenge that includes protecting data at rest, in transit, and during processing.
Encryption is the steel-reinforced door of our data house. It ensures that even if someone gets past the perimeter defense, they can’t figure out the data without the right key. Cloud providers offer a variety of encryption options, from server-side encryption for data at rest to SSL/TLS for data in transit. In this article, we talked about options for encrypting your data at rest.
But security doesn’t stop at encryption. It also includes identity and access management (IAM), ensuring that only authorized personnel can access specific data or applications. Think of IAM as a security guard at the entrance checking IDs before letting anyone in.
Moreover, regular safety audits and compliance checks are like routine building maintenance checks. As we continue to build and innovate in the cloud, these practices must evolve to counter new threats and meet changing regulations.
Bottom line: Always build a secure data fortress in the cloud
In this article, we have laid out the blueprint of cloud data management, from the core storage layer to the pinnacle of the presentation layer. Like building a skyscraper, each layer plays a critical role in ensuring the integrity and usefulness of your data. However, an architecture is only as good as its security measures, so it is important to ensure a high level of security at all levels.